The surprising decline of entrepreneurship and innovation in the West
The idea that we are living in an entrepreneurial age, experiencing rapid disruptive technological innovation on a scale amounting to a new “industrial revolution” is a pervasive modern myth. Scholars have written academic papers extolling the coming of the “entrepreneurial economy”. Policymakers and investors have pumped massive amounts of funding into start-up ecosystems and innovation. Business schools, universities and schools have moved entrepreneurship into their core curricula.
The only problem is that the West’s golden entrepreneurial and innovation age is behind it. Since the 1980s entrepreneurship, innovation and, more generally, business dynamics, have been steadily declining – particularly so in the US. As economist Tyler Cowen has found:
These days Americans are less likely to switch jobs, less likely to move around the country, and, on a given day, less likely to go outside the house at all […] the economy is more ossified, more controlled, and growing at lower rates.
The ossified economy
No matter what measure of entrepreneurship you use, the underlying trend is the same: downwards. For instance, measured as the ratio of new firms (those younger than one year) to total firms, then entrepreneurship in the US declined by around 50% between 1978 and 2011. In terms of the share of young firms (those younger than five years), entrepreneurship declined from 47% in the late 1980s to 39% in 2006. Meanwhile, people working for big firms (those employing more than 250 people) rose from 51% to 57% of the overall workforce and the average firm size increased from 20 to 24 people over the same period.
Job-to-job mobility, within job mobility and geographical mobility – all indirect measures of business entry and exit dynamics – have been declining. There is also evidence that after 2000, job creation in the US shifted from the creation of high-paying jobs to low-wage (low-skilled) ones. Similarly, the share of entrepreneurs with higher education in the US declined from 12.2% in 1985 to 5.3% in 2014. As economist Nicholas Kozeniauskas puts it, “the decline in entrepreneurship is concentrated among the smart”.
Several measures indicate that entrepreneurs are also less innovative. The ratio of patents to GDP in the US is declining and the cost of patenting is increasing. The age of inventors, when they registered their first patent, and the average size of research teams, are on the rise. Plus, as economist Nicholas Bloom and his co-authors have found, “research productivity for the aggregate US economy has declined by a factor of 41 since the 1930s, an average decrease of more than 5% per year”.
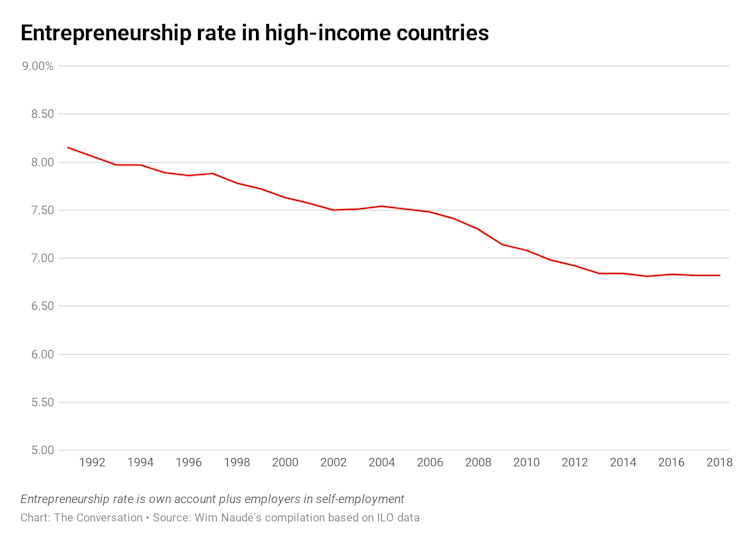
As well as being a problem in the US – the world’s largest and most complex economy – evidence also confirms that entrepreneurship and innovation are declining in Belgium, the UK, and Germany. And, as I found in a recent paper, ILO data shows a decline, from 8.2% in 1991 to 6.8% in 2018 in entrepreneurship in high-income economies.
Reasons for the decline
One reason for this decline is a fall in population growth and population aging. Europe’s fertility rate is 1.6 children per woman, which means that each generation will be 20% smaller than the previous one.
Another reason is growing market concentration. Incumbent firms have a growing amount of power that stops new ones from entering the market. Similarly, new competition is suppressed by the proliferation of so-called zombie firms. These are firms older than ten years that have low productivity levels and are often kept in business by subsidised finance. There may be more than 100,000 zombie firms in the UK alone.
These reasons are probably interlinked. Poor population growth means lower levels of demand, which encourages existing companies to profit as much as possible from their existing markets. This means they stifle the entry to new competitors and extract more profit by paying employees less. The increasing number of mergers and acquisitions, as well as decline in initial public offerings, with young companies preferring to be bought by large incumbents, reflects this too.
Based on the nature of the problem, the solutions to this entrepreneurial decline are straightforward: break up monopolies, improve competition, allow markets to work better, facilitate knowledge diffusion. Moreover, and vitally, it will require boosting overall demand. This means more investment by governments in public services and infrastructure, reducing high levels of inequality and improving the bargaining power of labour unions.
The case for these policies is overwhelming. But, unfortunately, it might not be as simple as this. In a recent paper, I argue that the fact that the decline in entrepreneurship is confined to wealthy and complex economies, suggest that this may be a price to pay for complexity.
As Geoffrey West has stressed, the same growth curve that characterises living organisms also applies to the growth of cities, economies and companies. After growing beyond a certain threshold, size and complexity stabilises and growth levels off. So it becomes more challenging to create and use new valuable knowledge once you reach a certain size. And, the more complex a production process is, the more that can go wrong.
But how concerned should we really be? Some scholars have questioned whether the decline in entrepreneurship is necessarily undesirable. They point out that the decline has been accompanied by more employment, more job stability and better job matching (where people find jobs that better fit their preferences and talents). It may also reflect that the most productive firms, which happen to be larger, are being allocated the most resources, which is good for the economy.
If indeed this is the case, then the downside may be that complex, ossified, modern economies will gradually become less flexible, less adaptable to external change – and hence more vulnerable. Survival will therefore involve finding ways to deal with systemic societal vulnerability.
Wim Naudé, Professorial Fellow, Maastricht Economic and Social Research Institute on Innovation and Technology (UNU-MERIT), United Nations University
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.

















