Britain’s electricity since 2010: wind surges to second place, coal collapses and fossil fuel use nearly halves
In 2010, Great Britain generated 75% of its electricity from coal and natural gas. But by the end of the decade*, these fossil fuels accounted for just 40%, with coal generation collapsing from the decade’s peak of 41% in 2012 to under 2% in 2019.
The near disappearance of coal power – the second most prevalent source in 2010 – underpinned a remarkable transformation of Britain’s electricity generation over the last decade, meaning Britain now has the cleanest electrical supply it has ever had. Second place now belongs to wind power, which supplied almost 21% of the country’s electrical demand in 2019, up from 3% in 2010. As at the start of the decade, natural gas provided the largest share of Britain’s electricity in 2019 at 38%, compared with 47% in 2010.
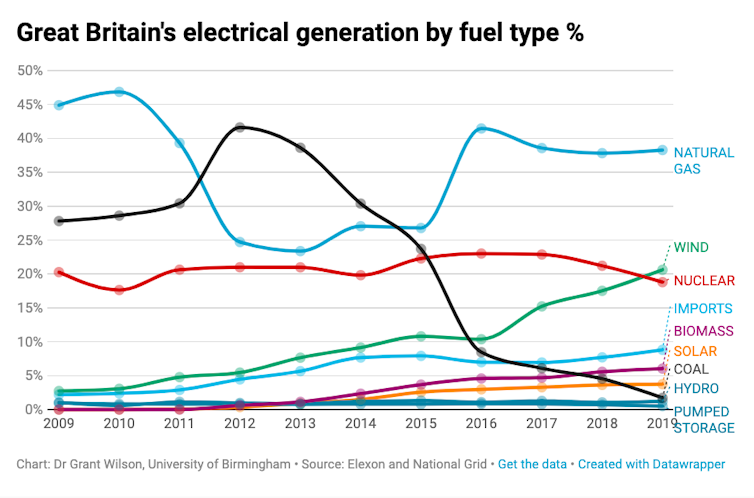
As we predicted last January, 2019 saw the annual total for coal generation drop below solar and into seventh place for the first time. Britain’s renewables also generated more electricity than coal and natural gas combined over a month for the first ever time in August.
Read more: Britain has shifted 30% of its electricity away from fossil fuels in just nine years
Besides the reduction in carbon emissions, there was another remarkable shift in Britain’s electrical system during the 2010s. The amount of electricity consumed fell by nearly 15% between 2010 and 2019, with the economy using 50 terawatt hours (TWh) less electricity in 2019 than it did in 2010. That’s enough electricity to power half of Britain’s cars and taxis, if they were all electric vehicles.
Some of this reduction can be attributed to greater energy efficiency, such as more LED lighting, and the fact that more goods were imported, rather than manufactured within Britain. With wages stagnant since 2010, it’s likely that lower economic demand also contributed.
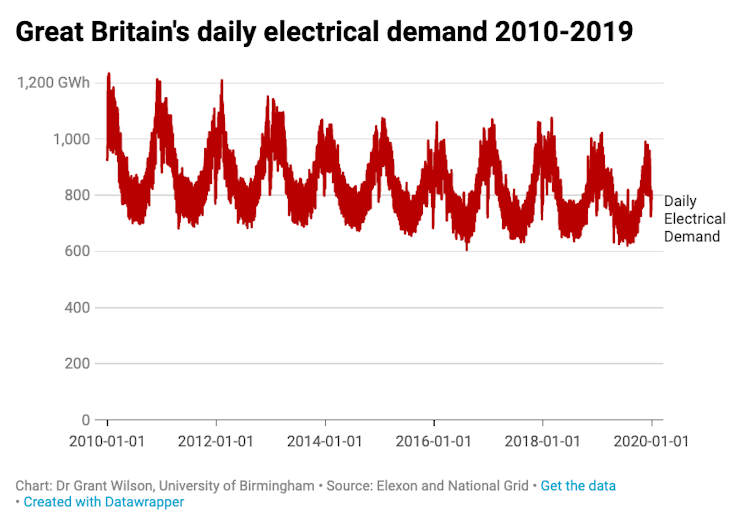
The rise of renewable generation and the fall in electrical demand allowed coal power to be transitioned off the system. Britain’s electrical grid was coal-free for over 3,700 hours in 2019, something that would have been unthinkable ten years ago.
Winds of change
Wind energy set a new record of 26.5% for December 2019’s generation in the UK. Including solar, hydroelectric and biomass, renewables provided nearly 37% of the month’s electricity overall, with wind energy reaching a peak of nearly 17 gigawatts (GW) during the afternoon of December 10.
Since August 2018, renewables have produced more electricity than nuclear power for 17 months straight. Nuclear fell to less than a fifth of electricity generation in 2019, its lowest level since 2008 due to extended maintenance periods at six nuclear power stations. This helped the annual output of wind energy to surpass nuclear for the first time in 2019.
But the 2020s will prove an even greater challenge for decarbonisation, not least as Britain’s economy is still heavily dependent on fossil fuels for transport, heating and hot water. Sales of electric vehicles in Britain are accelerating, with a quarter of a million now on Britain’s roads – but how to decarbonise heating is still up for debate.
Encouragingly, due to cleaner electricity, a major milestone for electric heating is likely to have been reached in 2019. Using electricity from the grid to heat buildings or hot water is less carbon intensive than burning natural gas to get one kilowatt hour (kWh) of heat from a modern gas boiler. This means that even a simple electric heater releases on average less carbon than burning natural gas.
But since natural gas demand varies greatly over a day and between seasons compared to the demand for electricity, a wholesale shift from natural gas to electricity is a significant challenge. Using low-carbon gases such as hydrogen is one option to decarbonise Britain’s heat supply, so too are electric heat pumps. Without a sustained focus on shifting heat and the transport sector from fossil fuels, Britain will fail to become a net-zero carbon economy by 2050.
What lies ahead in the 2020s?
Scaling up renewable energy generation has catapulted Britain through a decade of electrical system change, but to capitalise on this momentum in the 2020s, low-carbon energy must be complemented with low-carbon flexibility. That must mean the growth of industries focused on energy storage, demand reduction and management, and local control systems, ensuring the system can continue to meet demand at all times.
After a promising decade of decarbonisation - despite policy setbacks like the green deal – the race is on to be the first G7 country to attain a net-zero carbon economy. Showing that it is possible to fully decarbonise a large economy while remaining internationally competitive would send an important message to the world.
Read more: Climate change: six positive news stories from 2019
The next decade will see even more renewable energy deployed, such as the Hornsea Project One – a 1.2 GW offshore wind farm, due to be completed in 2020. But what else do the 2020s hold? Here are our energy predictions for the next ten years:
- Britain will install an additional 30 GW of marine energy generation, including offshore wind, wave, tidal flow and tidal range.
- Over 10,000 “active buildings” will be built. These are highly energy efficient buildings integrating renewable energy technologies for heat, power, and transport with different types of heat and electrical storage.
- Over 80% of new cars sold will be battery electric vehicles.
*The electrical generation data is from Elexon and National Grid. Data from other analyses (such as BEIS or DUKES) will differ due to methodologies and additional data, particularly by including combined heat and power, and other on-site generation which is not monitored by Elexon and National Grid. Renewables in this analysis = wind + solar + hydro + biomass.

Grant Wilson, Lecturer in Chemical Engineering, University of Birmingham., University of Birmingham; Iain Staffell, Lecturer in Sustainable Energy, Imperial College London, and Noah Godfrey, PhD in Chemical Engineering - Modelling Flexibility in Future UK Energy Systems, University of Birmingham
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
